Our modern world has plenty of marvelous discoveries and advancements. With technology, mankind continues improving and inventing brand-new things. There are several types of coatings offered which can be used to cover a plethora of surfaces. One example is antimicrobial coatings, which are truly a gift of science. These coatings are made of core materials that have many advantageous qualities. Yes, they impact the appearance of the surface area. Also, these coatings likewise play a considerable function in protection and avoidance. Antimicrobial coatings are used extensively to secure surfaces and human beings too. Get to know all the details with this guide of antimicrobial coatings, from the products utilized to benefits and risks.
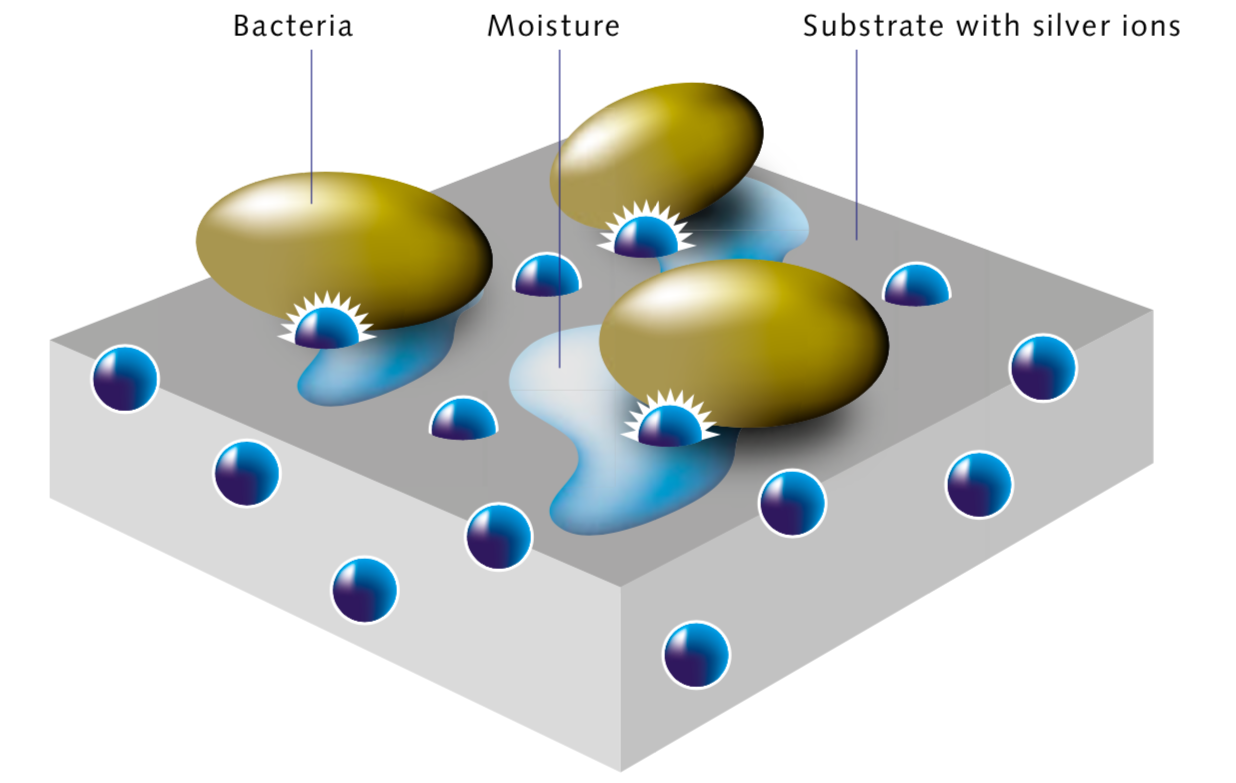
What is an Antimicrobial Coating?
Antimicrobial coatings utilize chemicals to prevent the growth of pathogens through cellular membrane perturbation. In layman’s terms, an antimicrobial coating is an application of a chemical representative on a surface area that can stop developing disease-causing microorganisms. Apart from increasing the surface area’s toughness, appearance, corrosion resistance, and so on, these coatings likewise safeguard from damaging disease-causing microorganisms.
What is the Need for Antimicrobial Coatings?
As exposed by the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control, more than 4 million people get a Healthcare-Associated Infection (HCAI) each year, which results in 37,000 deaths. Fighting HCAIs is a significant problem for the healthcare sector around the world. HCAIs are the 6th leading cause of death in western countries. In establishing countries, the circumstance is even worse.
There is a boost in the requirement to secure surfaces from bacteria and microorganisms. This is not just real for healthcare devices/surfaces. The requirement is more extensive. Everything is vulnerable to microbes from surfaces, devices, and walls to fabrics and food, ultimately discovering their way to human beings. It is not possible to constantly tidy, decontaminate, or use strong chemicals on surfaces to prevent bacteria growth. In this scenario, antimicrobial coatings seem to be the very best alternative. It is an easy process of coating the surface area with antimicrobial representatives, leading to a more secure and long-lasting service.

How Are Antimicrobial Surfaces Made?
Getting a surface that can impede the growth of microbes can be obtained through two approaches. The very first method is a physical modification, which comprises product modification and surface area roughness. The second technique involves chemical modification. Chemical modifications consist of grafting of polymers, superhydrophobic surfaces, use of nanomaterials and coatings. These coatings consist of self-cleaning coatings and coatings with antimicrobial ingredients. The safety level, market norms, and the specific use of the coated item are remembered when picking the ideal antimicrobial coating.
What Materials Are Used in Antimicrobial Coatings?

Graphene materials: Graphene products include antimicrobial materials like fullerenes, graphite, graphene oxides, beautiful graphene sheets, and graphite oxides. These materials can impact microbes’ development due to their interfering with the bacterial membrane, oxidative tension, and entrapment of microorganisms.
Graphene-like two-dimensional materials: Here, raw and chemically exfoliated MoS2 sheets are used as graphene-like, two-dimensional products owing to their antibacterial activities.
Polycationic hydrogel: Polycationic hydrogel includes an antimicrobial hydrogel based on dimethyl-decyl ammonium chitosan-graft-poly( ethylene glycol) methacrylate poly( ethylene glycol) diacrylate. The product is believed to cause microbial death.
Silver nanoparticles: Silver nanoparticles have a bactericidal effect within a 1-10 nm variety and are size-dependent.
Polymer brushes: There are three kinds of polymer brushes utilized in antimicrobial coatings: functionalized polymer brushes, brushes consisting of bactericidal polymers, and non-fouling polymer brushes.
Dendrimers: Dendrimers are utilized in antimicrobial coatings due to their ability to traverse the cellular membrane.
Copper and its alloys: Copper, in addition to its alloys like bronze, brass, copper-nickel-zinc, and cupronickel, are understood to be natural antimicrobial elements. These components can prevent the development of and ruin disease-causing microorganisms.
How Are Antimicrobial Coatings Tested?
There is no particular test discussed by the antimicrobial sector as a single test to prove the antimicrobial coating’s effectiveness. Nevertheless, numerous test approaches have been developed by various companies to meet market requirements. A few of these tests are coined by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC), Japanese Industrial Standard (JIS), and International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The tests help gauge the efficiency of an antimicrobial coating in combatting the development and survival of microorganisms.
These tests are created for particular fields of use, product, or antimicrobial innovation. As a result, it is hard to choose one approach. However, an example of standards is ISO 22196 (JIS Z 2001) for antibacterial coating by makers. Antifungal test approaches are ASTM G21 or AATCC Method 30, Part III. Likewise, ASTM E2149 is utilized to spot antimicrobial activity after one hour of direct exposure, and ASTM E2180 is utilized to detect the antimicrobial activity after 24 hours of direct exposure on textiles. Likewise, ASTM G21 is utilized to identify resistance versus black mold and fungi.
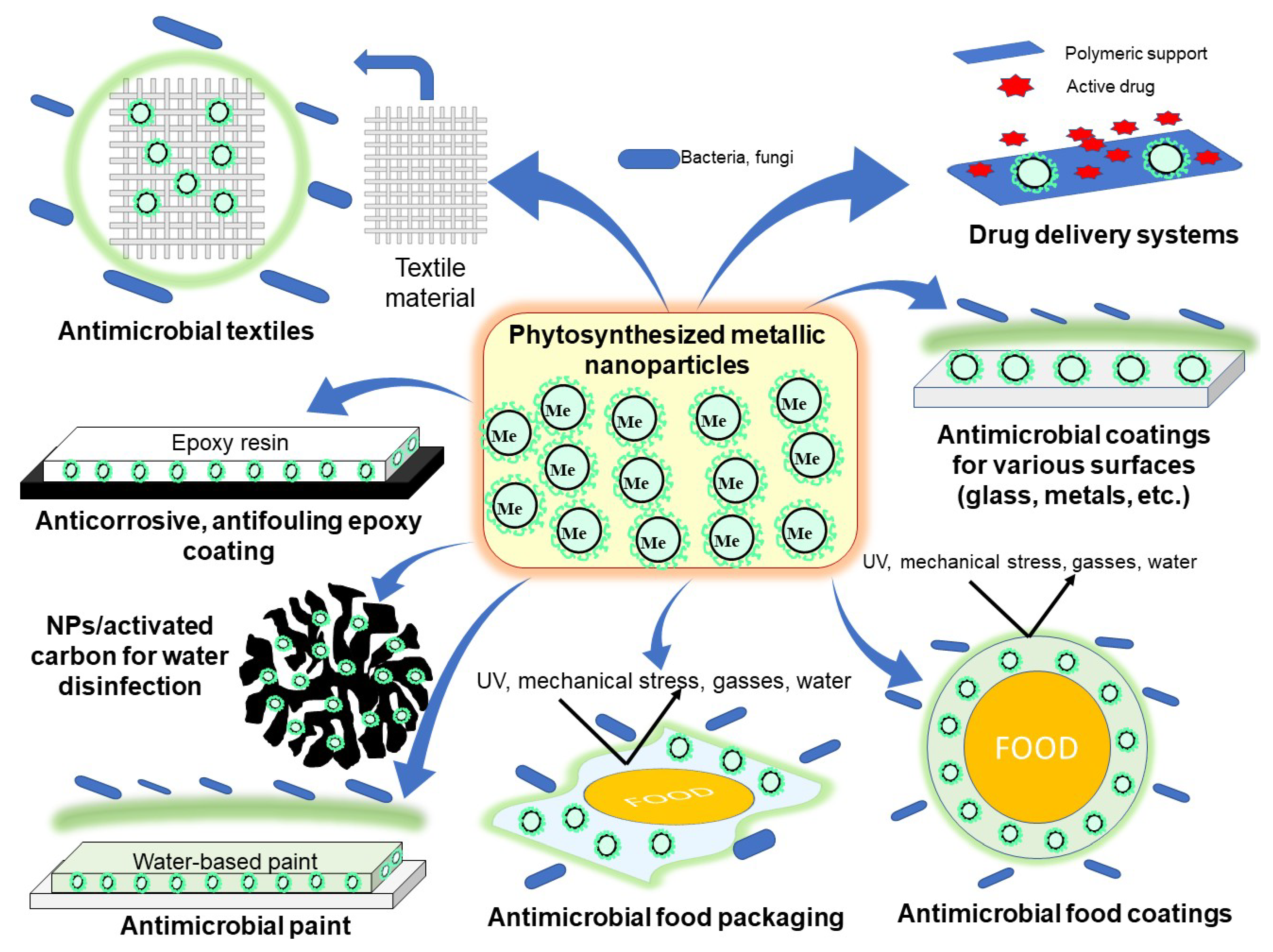
Where Are Antimicrobial Coatings Used?
Today, antimicrobial surface coatings discover use in several consumer and commercial applications, apart from the health care sector, such as:
- Industrial
- Commercial
- Building items
- Outdoors
- Housewares
An essential requirement of antimicrobial coatings is in the medical field. All health care facilities face the risk of HCAIs. Antimicrobial coatings assist in reducing the spread of germs through common areas like switches, doorknobs, etc. Even more, the coatings are utilized on catheters, surgical gadgets, electronic medical devices, medical instruments, trays, etc., to reduce the danger of infection during medical treatments. They are now even used for health center fabrics, including gloves, surgical masks, injury dressing, plasters, woven healthcare facility fabrics, and non-woven health center textiles. Innovation in the field has resulted in using these coatings in medical implants too.
Antimicrobial coatings are useful for various buildings like schools, office complexes, restaurants, public locations, and residential structures for long-term defense from disease-causing microorganisms. They are also utilized vastly in preserving the indoor air quality in air handling systems, like ventilation, heating, air-conditioning, ceilings, and fans. The coatings work in combating mold development and regrowth on various surfaces like automobile parts, walls, ceiling pipelines, etc.
Antimicrobial coatings have made their method into the food sector also, finding use in food processing units, dairy, massive production, and the utensils and containers used while doing so. In the fabric sector, they assist supply sturdiness, freshness, and stain resistance to fabrics.
What Are the Benefits of Antimicrobial Coatings?
As pointed out earlier, there is an overall growth in using antimicrobial coatings for not just the commercial and healthcare sectors where they are most required, however also for domestic use. Following are some of the advantages of these coatings.
Security Against Microbes
Most importantly, these surface coatings secure versus the development of various microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, algae, mold, and so on. Research has shown that the application of these coatings on surfaces prevents the growth of various microbes. A surface area ends up being an unfavorable environment for microbes to grow and survive as long as the coating is applied to it. It also causes preventing staining, any bad odor, or deterioration of the applied surface area.
Fewer Disinfectants Needed
Using antimicrobial coatings on surfaces reduces the requirement for extreme cleaning agents and disinfectants needed to handle stubborn microorganisms in public centers. This slowly causes a reduction in the ecological impact of using these cleaning up representatives in buildings, particularly medical centers.
Health and Cleanliness
Consider the case of a workplace, school, or hospital where there is a lot of individuals. There is a high likelihood of the spread of infections in such places. The presence of an antimicrobial coating on surfaces helps fight the spread of these infections or illness to a large degree. The coatings safeguard the high-volume tracepoints like doorknobs, switches, railings, and furniture. Even more, they contribute to tidiness by reducing the presence of germs and bacteria in the air.
Economical
Antimicrobial coatings help in reducing upkeep expenses. When the coating is used on a surface, it avoids staining, discoloration, leeching, or other elements that impact the object’s look. It saves the additional monetary burden and labor that would have been needed for the upkeep or replacement of these things.
Increased Lifespan
Defense from microbes paired with the upkeep supplied by antimicrobial coatings increases the general lifespan of items. They are secured versus discoloration, odor, and other damage triggered by microbial activity.
Infrastructure Value
The application of antimicrobial coatings not only secures surfaces but also adds to the infrastructure standard. The presence of these coatings makes it possible for organizations to provide a safer and cleaner environment for the people in it. Making use of these coatings on surfaces carries a more profound message that companies appreciate the safety and atmosphere that they supply to individuals. It certainly contributes to the value of the building and its overall facilities.
What Are the Risks of Antimicrobial Coatings?
While there are huge advantages of antimicrobial coatings, there are some drawbacks. The numerous threats connected with making use of the antimicrobial coatings on surfaces include the following:
The antimicrobial coating can release active components that may gradually go into the community, causing health hazards in the long run.
The active ingredients launched from the coatings, including silver, zinc, and copper, could have hazardous impacts on fish, shellfishes, algae, and so on. Human beings ultimately take in such harmful components taken in by fish.
Likewise, using antimicrobial coatings on materials to prevent microbial growth could lead to contaminants being presented in the wastewater, ultimately harming the marine environment.
The gradually infused and given off active nano-ingredients may lead to various or new adaptive microbes such as drug-resistant bacteria.
The majority of the above cases result from biocidal antimicrobial coatings that leach out components to kill microbes. Flora Coatings has established a biostatic antimicrobial coating called Invesil that does not seep components and is considered safe.
Safe Use
The Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks (SCENIHR) insists on ‘prudent use of antimicrobials.’ As a result, there has been a universal requirement for the style of safe antimicrobial coatings. It has caused the Safe-by-Design concept, which highlights the need for developing a product eliminating dangerous material. It highlights the control of the release of antimicrobial aspects from the coating. It might likewise be designed to target some specific microbes without harming the other bacteria. There is a need to utilize a suitable production procedure that looks after all the safety requirements. A research study has suggested the treatment of hospital wastewater to stop it from affecting marine life.
New technologies have developed with a different research study in the field. Polymers, safe bacteria-repelling surfaces, and other ingenious technologies have been used to reduce antimicrobial coatings’ negative effects. Products are now being designed with safety, benefit, and cost-effectiveness as a concern.
Today, innovation is used widely in the field of medicine with proper safety norms and utmost care. When it comes to medical implants in a body, there is a high chance of bacterial infection. Also, it is tough to get rid of and replace implants frequently. So before being put in a person’s body, medical implants are treated with non-toxic, bio-stable, and bio-compatible antibacterial agents.
What are Antibacterial and Antiviral Coatings?
It is popular that germs are living microorganisms that can be eliminated with antibacterial representatives, while a virus is a nonliving pathogen and can not be eliminated but only deactivated. Likewise, a virus has an adversely charged exterior membrane that can be damaged by solvents, specific UV frequencies, heat, spikes, extremely favorable charges, or metal ion interference. Most protonated solvents like alcohols and surfactants (or soaps) can break an infection’s exterior protein. When the protein is ruined, the infection can not attach to cells and transfer or alter human ribonucleic acid (RNA). Theoretically, the thickness of an antiviral coating needs to be more than the surface area’s average roughness. A lot of solid surfaces have a typical roughness in the micron range. It can therefore be presumed that an efficient coating would have a thickness in the micron variety. Numerous commercial items are claiming the deactivation of viruses through coating chemistry. However, the absence of proper screening protocols questions the precision of such claims.
What is the marketplace for Antimicrobial Coatings?
According to the Grand View Research Report, in 2015, the global market for antimicrobial coatings was estimated at $2.44 billion. The 2019 report states that the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.5 percent between 2019 and 2024. In 2019, the antimicrobial coating market achieved $2.8 billion, and by 2024, it is approximated to reach $5.4 billion. The antimicrobial coatings market is considered to increase significantly due to the current COVID-19 pandemic crisis. The demand for antimicrobial coatings comprises silver, copper, and other antimicrobial coatings.
The main application areas are:
- Medical
- Indoor air quality systems
- Mold removal
- Textiles
- Food and drinks
- Structure and construction
Worldwide federal governments are worried about HCAIs. So there is an increase in demand for antimicrobial coatings, which are considered to play an essential role in avoiding the spread of infections. The market is seeing stable growth in North America and Europe, where governments are taking significant steps in creating awareness about the utility of these coatings. The United States and Canada is the biggest market due to the high medical and living requirements in the United States. The federal government has enforced strict guidelines to handle HCAIs in North America and Europe. Silver antimicrobial coatings remain in high demand in North America. A few of the top manufacturers in the market of antimicrobial coatings are:
- ArmorThane Protective Coatings
- BASF
- AkzoNobel
- RPM International
- PPG Industries
- Sherwin-Williams
What is the Future of Antimicrobial Coatings?
The antimicrobial coating sector is brimming with activity. Research study and innovation continues to supply much better, more secure, and innovative antimicrobial coatings that are cost-effective. The factor behind the research is the consistent growth in demand in North American and European nations. There has also been an increase in demand in Asia-Pacific, Africa, Latin America, and Middle East regions.
Further, there is a massive cry for the controlled release approach. All these factors are resulting in a sharp increase in demand, coupled with development. Future antimicrobial coatings will need to fulfill all functions through combination. Likewise, the need for antimicrobial coatings will spread to increasingly more public structures. The future might see antimicrobial coatings in practically all structures as an easy method to keep bacteria away and maintain a healthy environment.
Conclusion
The rapid development of the antimicrobial coating market regarding demand and a call for enhancement is paving a course for a brand-new scenario in the market in the future. The industry is experiencing growth from multiple directions. On the one hand, there is a sharp boost in global need, owing to the rise in awareness about the advantages of these coatings, while on the other hand, market forces are putting pressure on carrying out more research study in the field, leading to better items in regards to safety and expense. Likewise, new products are being explored as well as new locations. It appears as if the antimicrobial coating sector is going to witness a historical transformation soon.

